
Indian banking sector is witnessing a decline in the credit-deposit ratio. This is easing liquidity pressures that had previously constrained credit expansion and elevated borrowing costs. The banking environment is stabilizing with credit growth is moderating from overheated levels while deposits growing at a robust clip.
This positive shift resulted from the RBI’s regulatory measures, rising deposit rates, and slower demand for credit. These developments have further balanced the monetary environment.
Improved Liquidity as Credit Deposit Ratio falls
Credit growth in India’s banking sector has outpaced deposit growth for many months. This has resulted in tight monetary conditions and elevated credit deposit rates. Among other things, this also led to high borrowing costs and limited the growth of banking sector.
But RBI’s recent data indicates relaxation in these conditions. The credit-deposit ratio has moved lower towards 78%. This decline also point towards the possibility that either the deposit accumulation began to match credit accumulation, or that the momentum of credit expansion has slowed, or both of these things.
The easing of liquidity conditions comes as a welcome respite to the banking sector, which was getting constrained on both growth and funding costs. It may also mark an inflection point for monetary transmission, which could help improve the effectiveness of the RBI’s policy actions.
Better credit-deposit ratios also help in stabilising the banking system, enabling a sustainable credit growth. This is crucial at a time when India is looking to maintain economic momentum as the world faces uncertainty.
Figure: Banking Credit Deposit Ratio Drops – Improving Liquidity
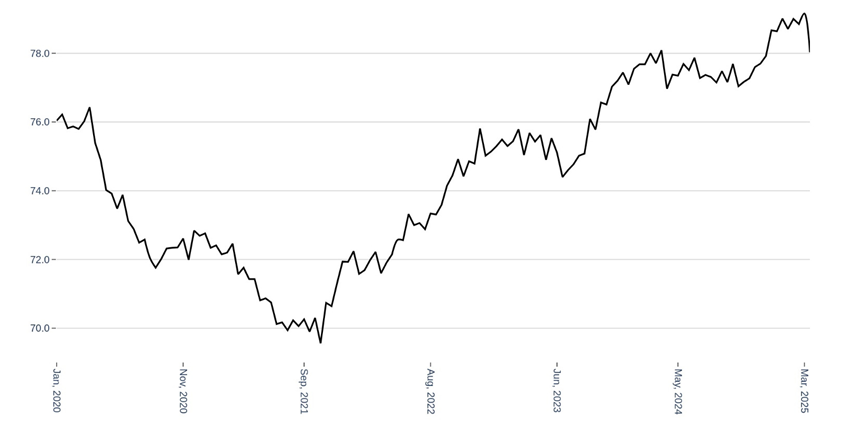
Source: RBI
Moderating Credit Growth – Sustainable growth or Slowing economy?
The latest dip in India’s credit-deposit ratio (CDR) is a positive shift in the underlying dynamics of the banking space. The CDR shows balance between incremental growth in aggregate credit and deposits.
A moderation in credit growth represents a significant change from the excessively hot conditions seen over the last year. During 2024, banking credit had jumped 20% on a year-on-year basis. This is supported by strong demand from corporates, retail borrowers as well as from services sector. The rapid growth was unsustainable and carries risks of asset quality deterioration and overheating in pockets of the economy.
Since then, credit growth has tempered to more sustainable levels, 10–12%, as a wider normalization of financial conditions has taken place. There are a couple of reasons for this:
Figure: Credit Growth Moderated to Healthier from Overheated Levels
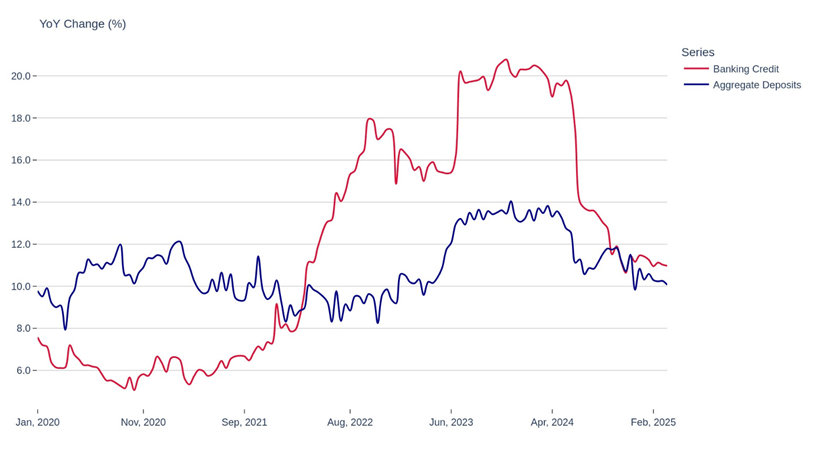
Source: RBI
RBI’s Tightening Measures
Credit growth was also brought down due to incessant efforts of the Reserve Bank of India. In the last 18 months, the RBI began a monetary tightening cycle, increasing the repo rate by 250 basis points to tame inflation. That made borrowing more expensive for both businesses and consumers, which naturally dampened demand for new credit.
In addition, the RBI announced some macroprudential measures to curb aggressive credit growth in a few high-risk sectors. This included:
Figure: Repo Rate is coming off and policy stance is turning accommodative
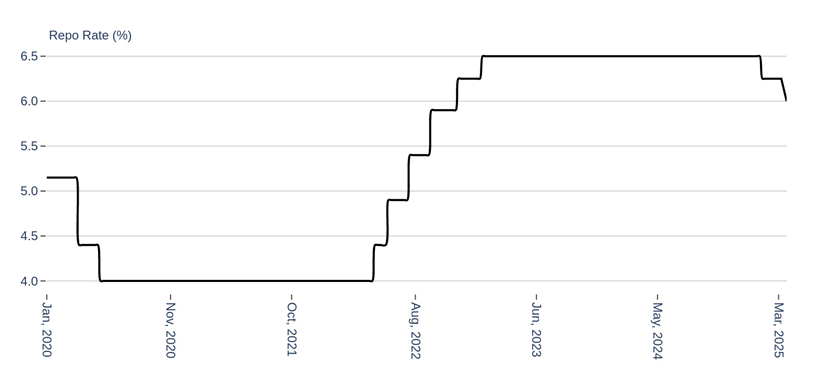
Source: RBI
Revival in Deposit Growth
On the balance sheet, deposits have begun to pick up, helped by higher deposit rates. Higher fixed deposit rates become increasingly attractive as inflation cools.
What to Watch for in the Coming Months:
RBI’s Monetary Policy:
Any change in RBI’s interest rate stand will be important here, particularly if inflation stays in check. What the central bank says about future rate actions will be crucial for credit demand and the liquidity of the banking sector.
Deposit Growth vs. Credit Demand:
Watch for upward movements in deposit growth, as higher deposit rates continue to draw savings. If deposit growth is strong, the liquidity pressures will continue to abate.
Related Tags

Invest wise with Expert advice
![]() IIFL Customer Care Number
IIFL Customer Care Number
(Gold/NCD/NBFC/Insurance/NPS)
1860-267-3000 / 7039-050-000
![]() IIFL Capital Services Support WhatsApp Number
IIFL Capital Services Support WhatsApp Number
+91 9892691696
IIFL Securities Limited - Stock Broker SEBI Regn. No: INZ000164132, PMS SEBI Regn. No: INP000002213,IA SEBI Regn. No: INA000000623, SEBI RA Regn. No: INH000000248
ARN NO : 47791 (AMFI Registered Mutual Fund Distributor)

This Certificate Demonstrates That IIFL As An Organization Has Defined And Put In Place Best-Practice Information Security Processes.