To understand how arbitrage works and how specifically arbitrage trading works, we will look at an example-based analysis of the initiation and closure of an arbitrage transaction. The focus is on understanding how arbitrage works as a process and how does arbitrage works in practice.
To understand how arbitrage works in general and to grasp how does arbitrage work in specific cases, we look at an illustration of cash futures trade. We look at the initiation of the arbitrage trade and the subsequent closure of the trade and the profit realization. Over to how arbitrage works and how does arbitrage works in practice.
At a conceptual level, arbitrage is the anomaly in pricing. In the good old days of the NSE and BSE, there used to be huge price differences between the two exchanges and even with the regional exchanges. Brokers would buy the stock at a lower price on one exchange and sell at a higher price on the other exchange. However, as markets became more efficient, this arbitrage trading vanished along with most of the regional exchanges.
With the introduction of futures came the cash-futures arbitrage strategy. Stock futures in India have monthly expiry cycles and expire on the last Thursday of each month. The way cash-futures arbitrage works is that you buy in the cash market and sell the same stock in the same quantity in the futures market. Since futures trade in minimum lot sizes, you must buy in the cash market also in equivalent lot sizes. Since futures price and spot price expire at the same level on the F&O expiry day, the difference or the future premium becomes the risk-free spread for the arbitrageur.
Structure of a real-time futures contract
Futures price, as the name suggests, pertains to a contract that is typically 1 month down the line. Hence there is the cost of carrying, which is like the interest cost in the case of cash-settled stock futures. In commodities, the cost of carrying includes storage, transportation, and insurance, but since stock futures are cash-settled, there is only interest as the cost of carrying. Normally, returns on cash-futures arbitrage are closer to 6-8% annualized.
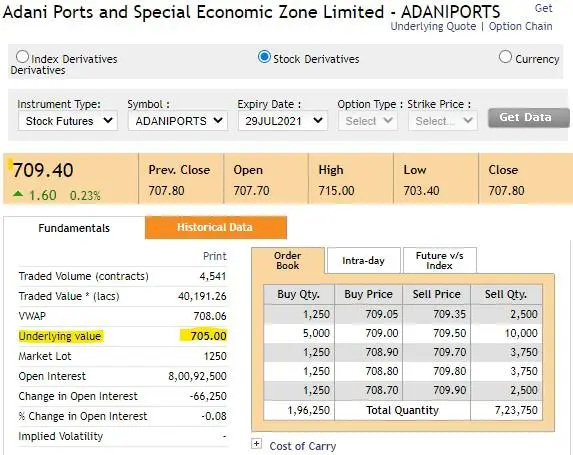
Let us now go to the next step and understand cash futures arbitrage trading with a live example. Here we look at the live price data of Adani Ports for Jul-21 Contract futures.

Source: NSE
In the above live price chart of Adani Ports, the cash price on 02 July is Rs.705.00 while the July 29th Futures price is Rs.709.40. So, the arbitrage spread is {(709.40-705.00)/705.00} which works out to 0.62%. That is the return for 1 month. So, the annualized return in this case works out to {(1+0.62%)12 – 1} = 7.70%
Normally arbitrageurs are happy with an annualized return of around 7-9% as they normally compare these returns with liquid funds, which give just about 4-5% returns. For cash-futures arbitrage, the trader will buy 1250 shares of Adani Ports in the cash market and simultaneously sell 1 lot of Adani Ports futures equivalent to 1250 shares in futures.
Realizing the profits on an arbitrage position
How is the trade unwound in an arbitrage?
In arbitrage trade, you buy in cash and sell in futures. That means you are long on equities and short on futures on the same stock and in the same quantity. You just unwind arbitrage by reversing positions either on the expiry date or before that if you get a good spread.
| Arbitrage Trade | Amount |
|---|---|
| The cash price of Adani Ports (purchased) on 02 July 2021 | Rs.705.00 |
| July Futures price of Adani Ports (sold) on 02 July 2021 | Rs.709.40 |
| Cash Futures spread | Rs.4.40 (0.62%) |
| Annualized spread on arbitrage | 7.70% |
| How will this arbitrage position get unwound on the expiry date | |
| The cash price of Adani Ports on Jul 29 | Rs.723 |
| July Futures price of Adani Ports on Jul 29 | Rs.723 |
| Cash Futures spread | Rs.0 |
| Profit on Adani Ports Cash Position | Rs.18.00 (723.00-705.00) |
| Loss on Adani Ports Futures Position | Rs.(-13.60) (709.40-723.00) |
| Net profit/loss on arbitrage | Rs.4.40 |
You have realized the assured spread of Rs.4.40, which you locked on the arbitrage day. This is done by unwinding the cash and the futures position. You can interpret this as the assured arbitrage realized or the spread encashed. It means the same thing. Remember, in this case, you are indifferent to the market price of Reliance. Irrespective of whether the stock closes 20% higher or 20% lower, your profit of Rs.4.40 or 0.62% is assured. Of course, the actual return will be lower as there are brokerage and statutory charges to contend with. Hence you need to factor those costs into your arbitrage calculation.
In practice, it is normally short futures being rolled over
The unwinding of futures looks simple but it is practically never done. Normally, the cash position is held on to and the short futures position is rolled over each month. Since the next month’s futures is always at a premium to the current futures, the short roller will earn the spread. So, the arbitrage trader holds on to the cash market position and keeps rolling the short futures position each month, just earning the spread and pocketing the profit on the short roll spread each month. This is also more efficient from a taxation perspective
In India, the most popular cash futures arbitrage works on the interest cost concept wherein the arbitrage spread is defined by the opportunity cost of funds or the prevalent interest rates in the market.
Arbitrage makes the market more efficient and smoother and better parity in prices. Arbitrage also makes the market safer and provides the institutions with a methodology of earning regular and fixed assured returns with low risk. They can put their large capital to use. Price discovery is also better due to arbitrage.
In arbitrage, you earn profits either by unwinding the arbitrage position or by rolling over the futures short position while holding on to the cash market position. There is also opportunistic closure of position when volatility forces a discount in futures.
Arbitrage profits would only work when there is price differentials between two markets for the same asset class. One more condition for arbitrage profits is that there should be a string of arbitragers who are constantly making the markets safer by arbitraging our differences.
Arbitrage is based on the principal of one price and the volatility that temporarily deflects from this law. Arbitrage also presupposes low levels of brokerage and low latency trades using advanced techniques of algorithms since such arbitrage trades are not possible manually.
![]() IIFL Customer Care Number
IIFL Customer Care Number
(Gold/NCD/NBFC/Insurance/NPS)
1860-267-3000 / 7039-050-000
![]() IIFL Capital Services Support WhatsApp Number
IIFL Capital Services Support WhatsApp Number
+91 9892691696
IIFL Capital Services Limited - Stock Broker SEBI Regn. No: INZ000164132, PMS SEBI Regn. No: INP000002213,IA SEBI Regn. No: INA000000623, SEBI RA Regn. No: INH000000248, DP SEBI Reg. No. IN-DP-185-2016, BSE Enlistment Number (RA): 5016
ARN NO : 47791 (AMFI Registered Mutual Fund Distributor), PFRDA Reg. No. PoP 20092018

This Certificate Demonstrates That IIFL As An Organization Has Defined And Put In Place Best-Practice Information Security Processes.